What is IBD?
The term ‘Inflammatory Bowel Disease’ (IBD) is a collective noun used to describe a group of disorders that primarily affect the digestive system. The two main types of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Other IBDs include Indeterminate colitis, Microscopic colitis and Behçet's disease.
Crohn's disease: This is a prevalent form of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) that primarily impacts the gastrointestinal tract. It is characterised by recurrent episodes of inflammation that can manifest in various areas along the digestive tract, spanning from the mouth to the anus. Although it can impact any part of the gastrointestinal system, it typically targets the small intestine and the initial section of the large intestine, known as the colon.
Ulcerative colitis: As with Crohn's disease, this is characterised by persistent inflammation in the gastrointestinal wall. It is, however, considered to be a distinct form of IBD because it specifically impacts the colon and rectum, whereas Crohn's disease can impact the entire gastrointestinal tract.
Indeterminate colitis: This is a form of IBD where the characteristics of the disease cannot be clearly classified as either Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. It may exhibit features of both conditions or present with ambiguous diagnostic findings.
Microscopic colitis: This refers to a type of IBD characterised by chronic inflammation of the colon. It is diagnosed through microscopic examination of colon tissue samples, as the inflammation may not be visible during a colonoscopy. Microscopic colitis is further divided into two subtypes: collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis.
Behçet's disease: This is a rare type of IBD characterised by recurring inflammation of blood vessels in various parts of the body. Although it predominantly affects areas such as the mouth, eyes and genitals, it can also impact the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in symptoms similar to those seen in Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. This chronic condition is believed to involve an abnormal immune response that causes widespread inflammation in the blood vessels.
Symptoms of IBD
The most common symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease are as follows.
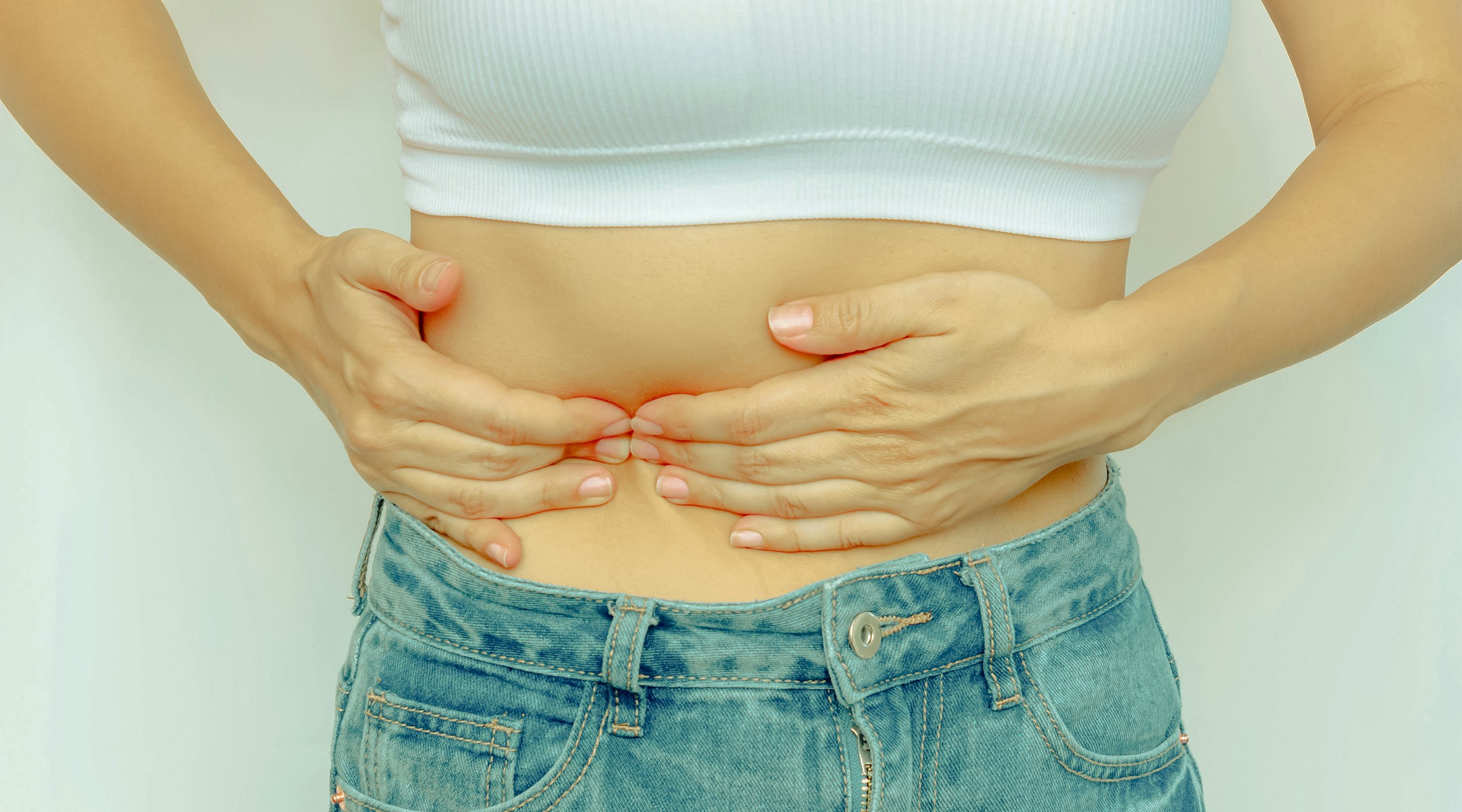
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Diarrhoea
- Rectal bleeding (blood in stools)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Anaemia (often manifested as paleness and/or fatigue)
- Fever
- Joint pain
- Skin problems (e.g. rashes, sores, or ulcers).
Please note: Symptoms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) will typically vary depending on both the condition and the individual. Also, symptoms and their severity often change over time. This is why it's so important to get medical help at an early stage and to work in collaboration with your doctor to determine the right treatment options for you.
The relationship between CBD and IBD
CBD engages with the body's endocannabinoid system, a vital regulatory system involved in managing numerous physiological processes, such as inflammation and immune response. In the case of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), the immune system erroneously targets the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in persistent inflammation. CBD has shown potential to influence this immune response and mitigate inflammation within the digestive system.
Research studies on the effectiveness of CBD in treating IBD
Several research studies have investigated the effectiveness of CBD in treating IBD and have shown promising results. For example, Daniele De Filippis et al. found that CBD treatment reduced inflammation and damage in the colon of mice with colitis, a form of IBD. In a different study, researchers found that CBD potentially reduced inflammation and improved symptoms in patients with ulcerative colitis.
Additionally, a review examined numerous studies on CBD and IBD and concluded that CBD has the potential to alleviate inflammation, pain, and other symptoms associated with IBD. It also highlighted CBD's ability to regulate the immune response and restore balance to the gut microbiota, which is often disrupted in individuals with IBD.
How to take CBD for IBD
While CBD holds promise in managing symptoms of IBD, it should not be seen as a complete substitute for conventional medical treatments. Instead, it is more likely to be beneficial as a complementary approach when administered in conjunction with the guidance of a healthcare professional. They will have the expertise to provide personalised advice on how to incorporate CBD into your treatment plan effectively and safely.
Before deciding to take CBD for IBD, there are four key points you should consider.
Dosage recommendations: CBD dosage recommendations for IBD can vary based on individual factors such as symptom severity, personal response and the concentration of the CBD product being administered. It's preferable to work with a healthcare professional to determine the dosage that's right for you. At a minimum, start with the lowest, possible dose and increase it gradually, if necessary.
Methods of using CBD for IBD: There are different methods of consuming CBD, including oral ingestion, sublingual administration, topical application and inhalation. Oral forms, such as CBD oil or capsules, are commonly prescribed for IBD. Sublingual administration involves placing CBD oil or tincture under the tongue for faster absorption. Topical CBD creams or ointments can be applied directly to affected areas. Inhalation of CBD through vaporisers cuts out the vast majority of health concerns connected to smoking, and offers the fastest onset of effects.
Side effects: Although CBD is generally well-tolerated, it's important to be aware that some individuals may experience certain side effects. These can include fatigue, changes in appetite, dry mouth, diarrhoea, or nausea. It's crucial to monitor your body's response to CBD and make note of any adverse reactions.
If you do experience side effects, you may need to adjust your dosage or explore alternative methods of consumption. Consulting with a healthcare professional who is knowledgeable about CBD can provide valuable guidance on managing and minimising potential side effects. They can help you assess whether the observed side effects are normal and within an acceptable range, or if further adjustments are necessary.
Safety considerations: When using CBD for IBD, it's crucial to ensure product quality and safety. Look for CBD products that have been tested by third-party laboratories for potency and purity. Avoid products with additives or contaminants. It's also important to consider potential drug interactions, as CBD can interact with certain medications. Consulting with a healthcare professional, especially if taking other medications, is advisable to minimise risks and ensure compatibility.
CBD and IBD in brief
CBD has shown potential in providing relief from both the inflammation associated with IBD and the accompanying symptoms. However, it is crucial to take CBD in a safe and effective manner. This requires personalised guidance from a healthcare professional who can consider your unique circumstances, lifestyle, and medications.
If you, or one of your loved ones, are suffering from IBD related issues and would like to know more about medicinal cannabis and the potential relief it may bring, we are here to help. At Releaf, we believe that access to medical cannabis is indispensable. That's why we offer tailored monthly packages based on your cannabis prescription, specialist consultations for medical cannabis, and a unique medical cannabis card for protection.